What is OSI Layer? It's Types
What is OSI Layer? It's Types
The OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) model is a way of
describing how different devices communicate with each other over a network. It’s
is developed by the ISO.
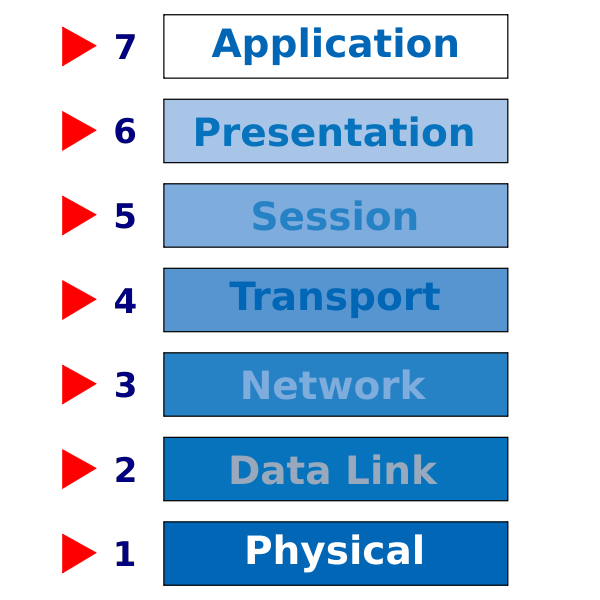
The OSI model is used in the field of networking to provide a standardized way of understanding how devices communicate with each other in a network. The OSI model is divided into seven layers, each with its own specific set of functions. These layers are arranged in a hierarchical order, with each layer building on top of the one below it. The seven layers of the OSI model are:
7. Application layer
6. Presentation Layer
5. Session Layer
4. Transport Layer
3. Network Layer
2. Data Link Layer
1. Physical layer
Note:
You can remember above point just like this All People Seen To Need Data Processing
A - Application Layer
P - Presentation Layer
S - Session Layer
T - Transport Layer
N - Network Layer
D - Data Link Layer
P - Physical Layer
Describe Above point in detail
7. Application Layer:
- Provides high-level services and protocols to end-users.
- Enables communication between software applications running on different devices.
- Defines protocols and standards for common applications to ensure interoperability between devices.
- Implements
protocols such as HTTP, FTP, SMTP, and DNS.
Supports application-level services such as file sharing, email, and remote login. -
Supports application-level services such as file sharing, email, and remote
login.
6. Presentation Layer:
- Provides data representation and manipulation services.
- Translates data between different data formats and character sets.
- Handles data encryption, compression, and formatting.
- Enables data conversion between different data types.
- Provides services such as data compression, encryption, and decryption.
5. Session Layer:
- Establishes, manages, and terminates communication sessions between devices.
- Provides synchronization and checkpointing, allowing devices to resume communication after an interruption.
- Handles security and authentication of communication sessions.
- Provides session management and control such as opening and closing
sessions.
- Supports remote procedure calls and virtual terminal access
4. Transport Layer:
- Provides reliable and transparent data transfer between devices.
- Ensures data integrity, flow control, and error recovery.
- Manages connections between devices and multiplexing of data streams.
- Can provide segmentation and reassembly of large data sets.
- Implements transport protocols such as TCP and
UDP.
3. Network Layer:
- Provides logical addressing and routing of data between devices on different networks.
- Determines the best path for data to travel between devices.
-
Handles addressing and packet switching, as well as congestion control and
traffic prioritization.
- Translates logical addresses into physical addresses.
- Implements routing protocols such as RIP, OSPF, and BGP.
2. Data Link Layer:
- Transfers data between directly connected devices on the same network.
- Divides the data into frames and adds header and trailer information to each frame.
- Performs error detection and correction, flow control, and manages access to the communication medium.
- Provides MAC addressing to uniquely identify devices on the network.
- Defines the protocols for error recovery and retransmission of lost frames.
1. Physical Layer:
- Transmits
raw data bits over a communication channel using physical devices and media.
- Defines the specifications for physical connections, such as voltage levels, bit rates, and transmission distances.
- Handles the electrical and mechanical characteristics of the interface between devices, including the cables and connectors.
- Specifies the transmission mode such as simplex, half-duplex, and full-duplex.
- Provides physical addressing to identify devices on the network.







If you have any dough, please let me know